-
Cosmedocs| Non Surgical
-
COSMESURG| Surgical
-
HARLEY STREET| Skin Care
FORMULATIONS -
| Skin Bar Clinic
 GLOW & GO
GLOW & GO
Treating melasma with chemical skin peels in dark-skinned patients
Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation also known as ‘chloasma’ and ‘pregnancy mask’. It is a common condition of skin in adults that appears in the form of dark brown or greyish colour pigmentation patches, which mainly targets facial skin. The name melasma is derived from the Greek word ‘melas’, which means black. Melasma occurs most commonly in women, especially pregnant women and people who live in warmer and sunnier climates.
It is a skin disorder characterised by dark skin patches distributed consistently on areas of the body that are primarily exposed to the sun. It is predominantly present in people who have the Fitzpatrick skin type IV-VI,which includes Hispanics, Africans, Asians and American Africans, and causes severe psychological, emotional and social distress.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Although there are numerous contributing factors that play their role in the pathogenesis, the exact cause and the etiology of the condition is yet to be understood.
However, the most common factors that contribute to the development of melisma, include sun exposure, pregnancy, genetics, intake of oral contraceptives, thyroid diseases and some drugs, such as anti-epileptics. The main cause of excessive skin pigmentation is an increased the number of melanocytes and excessive melanin production.The vascular component has also been considered to play a role in the development of melasma.
Clinical and Histological classification of melasma
There are three identified with melisma that have been identified, including:
- Malar:this mainly targets the cheeks and nose
- Centrofacial:targets the forehead, cheeks, nose and upper lip area
- Mandibular:mainly targets the jawline
Melasma has histologically been classified in three distinctive patterns, according to the primary pigmentation accumulation locations, including:
- Epidermal: well-defined borders and dark brown colour
- Dermal: ill-defined borders and light brown or bluish colour
- Mixed: the most common combination of colours, including bluish, dark and light brown patches
Available Treatment options
There is a range of treatment options available that range from topical applicators to photo protections, lasers,chemical skin peels and others.
- Sun protectionisa must to prevent a further darkening of the skin. A daily use of strong sunscreen protection with SPF 30 or higher is recommended
- Topical treatments (skin lightening products)aims to prevent further formation of pigmentation by suppressing melanin formation by melanocytes
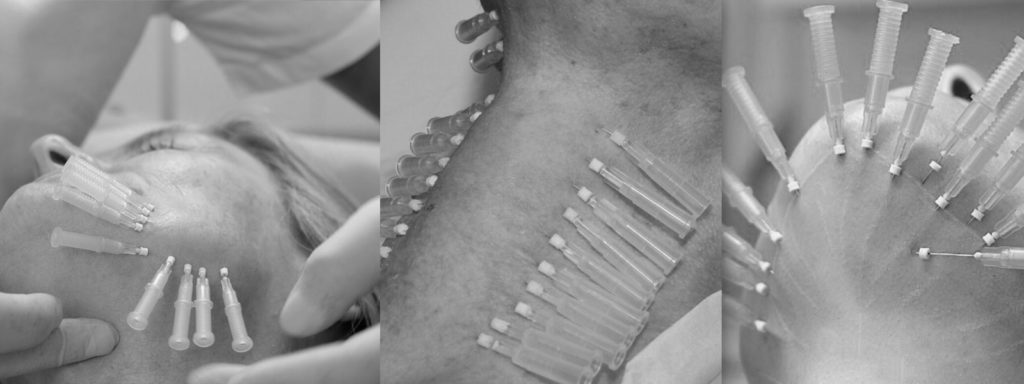
- Chemical skin peel, microdermabrasion treatmentscan remove melasma by removing the pigmented layers of skin that have excessive pigments through exfoliation. However, these treatments should be performed by an experienced practitioner, as they can even make the pigmentation worse
- Laser treatments: The lasers work by removing the outer skin layer or by specifically targeting the pigmentation that produces skin cells. It gives similar results to that of chemical peels or microdermabrasion
It has been observed that a combination of 2 or 3 treatments produces better results than administering a single pigmentation treatment, butdespite this, the melasma treatment remains a challenge because only mild to moderate improvements are achievedin the majority of patients.
Treating melasma in dark-skinned patients
A Fitzpatrick Skin type scale is used to determine the type of skin. In this rating scale, the darker skin tone falls between type IV to Type VI. This type of skin provides better protection against photodamage, but is vulnerable to disorders of pigmentation, such as melasma.
This type of skin has a higher tendency for Post Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation(PIH). This is a type of pigmentation that results from an injury to the skin or is by a skin inflammation, such as photodermatitis, and is most common in darker-skinned people. Itis a limiting factor when pigmentation treatment procedures, like chemical skin peels and lasers, are performed, andit is therefore of the utmost importance to prevent and manage post inflammatory hyperpigmentation following melasma treatment, including chemical skin peels.
Chemical skin peels suitable for treating melasma
Chemical skin peeling treatment involves the application of a chemical on the skin that induces a controlled damage to some parts of the epidermis or the entire epidermis along, with or without damage to the dermis, causing skin exfoliation and the superficial lesions removal. This process is followed by the regeneration of new epidermis and dermis tissues.
Chemical skin peel treatment is a popular option for treating melasma. The treatment generates a controlled chemical burn to the skin that results in the elimination of unwanted melanin. Chemical peels have proved to be an effective treatment for melasma, both as a stand-alone treatment, as well as in combination with topical treatment.
Types of chemical peels for treating melasma in darker skin
Though there are an extensive variety of chemical peels available, the choice is limited when it comes to the treatment of Fitzpatrick type IV to VI patients, because the deeper chemical peels are not appropriate for use on dark-skinned patients as the risks of developing prolonged pigmentation are high. Even the use of medium depth peel should be done with caution.
Melasma Area and Severity Index (MASI) is a scoring system that is used for assessing the severity of the disease and for a treatment response measurement of melasma.
- Alpha Hydroxy Peels
The most common type of alpha hydroxy peel used for treating melasma is glycolic acid (GA). Generally, 30%-70% of GA solution is used for chemical peel treatment. After conducting a test peel, GA peel is performed at an interval of 2-3 weeks for 3-5 minutes. The peel is neutralised with water or with 1% solution of bicarbonate. Studies have supported its effectiveness in treating melasma with a significant reduction in the MASI scoring.
Lactic acid has similar effects as GA peel, but surprisingly it has not been used frequently for melasma treatment.
- Alpha Keto Peels
In recent years, pyruvic acid has gained significant attention for treating various skin conditions.
Advantages
Pyruvic acid peel possesses a range of properties, including:
- Kerolytic
- Sebostatic
- Anti-microbial characteristics
- It is capable of stimulating new collagen and elastin fibres within the skin
- It is effective for treating acne, sun damage and superficial scarring on the skin
- It is also effective in treating a variety of pigmentary disorders among light-skinned people
Disadvantages
- Pyruvic acid can cause intense skin burning, which has limited its use as a peeling agent for a variety of conditions
In a recent study, an innovative, non-erythematogenic pyruvic acid formulation was used to treat sun damage, superficial scarring and melasma. The study’s results showed that the peel was effective in all the three skin conditions, without any burning to the skin during or after the peel sessions. However, the studies about the use of pyruvic acid peel are limited to the Fitzpatrick skin type II-IV, so it still remains unanswered whether it works well on ethnic skin or not.
- Beta Hydroxy Peels
Salicylic acid falls into the category of acids that have traditionally been used for treating acne, melasma and PIH. The commonly used concentration of salicylic acid is 20%-30%.
Advantages
- Salicylic acid ethnol solutions are outstanding peeling agents for treating a variety of skin conditions in dark-skinned people, including melasma, acne and PIH
- It is oil soluble, so it penetrates deeper into the skin, unclogging pores and preventing acne breakouts
- Salicylic acid possesses anti-inflammatory properties, so it reduces PIH following skin peel treatment
- It produces a diffused skin whitening effect
Disadvantages
- It can cause deep skin burns when used in a higher concentration or applied for a longer time
- It does not produce long-lasting results and requires regular use
- If higher amounts of salicylic acid get absorbed into the skin, it can cause salicylate toxicity
- Combo Salicylic and Mandelic acid peel
It is a unique combination of AHA and BHA that has not been tried widely yet.
- Mandelic acid is the largest of the AHAs. It penetrates slowly and evenly through the epidermis, which makes it ideal for sensitive skin
- Salicylic acid, on the other hand, penetrates quickly through the skin, while also providing an extra advantage of reducing the PIH
These properties, when combined together in the form of a skin peel, make it an effective skin peeling combination, particularly for ethnic skin. This combination works really well for numerous skin conditions, including acne, pigmentation, acne scarring and melasma. Although there is no clinically published data available for melasma,the salicylic and mandelic combo peel has proved to be much more effective compared to the GA peels for active acne and post-acne hyperpigmentationand with fewer side effects.
- Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) peel
Trichloroacetic peel is more frequently used for lighter skin and is less used on darker skin because of the higher risks of scarring, as well as post-peel dyschromias. This peel, when used in a low concentration of 10%-35%, is preferable, as it only reaches the upper papillary dermis. So these peels are unsuitable for treating dermal melasma and its mixed forms on dark-skinned patients.
The TCA peel may prove to be effective, like GA peels, for treating pigment dyschromias but caution should be taken while using these on the darker skin tones due to the higher prevalence of side effects. It can cause hyper or hypopigmentation.
- Jessner’s Peel
This skin peel uses a combination of salicylic acid, lactic acid, and resorcinol mixed in ethanol. It has been used widely as a superficial peeling agent for all types of skin.
A recentnew development in Jessner’s peel uses a combination the medium depth peels along with other peeling agents, such as GA and TCA peel.
Advantages
- A combination of Jessner’s peel with TCA solution provides a more even penetration and is an outstanding skin peel, as it has a low and safe concentration of TCA
- It improves the overall complexion, while reducing the appearance of acne scarring and assistingthe treatment of melasma
- It is a versatile peel that unclogs pores, kills bacteria, reduces acne, corrects uneven skin tone, sun damage and melasma
Disadvantages
- The primary risk involved in the use of Jessner’s peel for dark skin is PIH
- It can also cause ochronosis (a peculiar kind of skin discolouration)
- It is not recommended for use on dark-skinned individuals
- Tretinoin peels
The working oftretinoin peels is considered to be same as that of topical tretinoin applications.
- It causes epidermal changes and disperses melanin
- A comparative research study was conducted on dark-skinned patients being treated for melasma to determine the effects of 1% tretinoin peel with a 70% of standard GA peel.The results showed that the use of tretinoin peel led to a fall in the MASI index scores that was similar to when standard glycolic peel was used, but with few side effects.
- Newer kinds of peels
Despite the popularity of traditional skin peeling agents, researchers have continued to explore the newer peeling agents for treating numerous pigmentary dyschromias, including melasma.
- Phytic acid peel
One chemical agent that deserves mentioning in this regard is phytic acid peel.
- One of the problems associated with the use of alpha hydroxy acid peels is that they need to be neutralised and the exact duration of neutralisation needs to be defined
- Phytic acid offers an easy solution for this problem. It is a form of alpha hydroxy acid with low pH and does not require neutralisation, so there is no danger of overpeeling
- Phytic acid peel causes continuous and successive actuation of its acids in an unaggressive manner, soyou don’t get the skin burning sensation you experience with glycolic peel
- Phytic acid peel solution can be left on the skin until the next morning, unlike other kinds of AHA peels, which require instant neutralisation
- Generally, a once a week application of phytic acid peels is recommended, but if a more stimulative effect is needed, it can be applied twice a week
- In order to achieve skin lightening, 5-6 peeling sessions are required
- Phytic acid is a safe and effective treatment for melasma among dark-skinned individuals, but it requires additional assessment
- II. Amino Fruit Acid (AFA) Peels
- These are potent antioxidants
- AFAs has been found to be highly effective in anti-ageing cosmeceuticals and works against photopigmentation.
- A comparative study of glycolic acid and AFA peels showed that the latter peels give better results than GA peels for treating melasma, as there is less irritation and better tolerance
- There is still a need for studies of dark-skinned patients to develop their efficacy for treating melasma
III. Cocktail Skin Peels
- This is a newer generation of peels that use a combination of different peeling agents with the skin rejuvenating ingredients, like antioxidants, astringents, antiseptics etc
- It is a one-step skin peeling solution that treats multiple skin conditions and can be used safely for all types of skin and tones
- These peels range from superficial to deep peels in their depth
- Peel to Reveal (P2R) by Harley Street Formulations
This is a unique and innovative example of cocktail skin peels. It is a perfect combo of potent skin peeling agents with skin rejuvenating ingredients, which include TCA, salicylic acid, lactic acid, combined with numerous skin brighteners, as well as antioxidants such as glutathione, mandelic and azelic acid, as well as fruit extracts,among others. The P2R peel possesses powerful ways of treating multiple skin conditions, including pigmentation and sun damage.
The role of priming agents in skin peeling
As has already been mentioned, the primary drawback of using chemical peels for treating melasma in dark skin is post inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), which may occur during or after the treatment sessions. There are various suggestions for addressing this problem, but priming or preparing skin for the treatment is the most useful measure. Thisdoes not just help to decrease PIH, but also enhances the effects of the skin peeling ingredients.
- The benefits of priming
- The priming procedure involves an application of topical depigmentary ingredients, such as tretinoin, hydroquinone or GA almost two weeks before the application of skin peel
- It assures uniform active ingredients and peeling agent penetration in the skin, while also accelerating the healing process and maintaining its effects on skin obtained through the chemical skin peel
- It reduces and prevents post-treatment side effects and complications, particularly PIH
Prevention of relapse
Another issue that arises while treating melasma in dark-skinned patients is the high vulnerability of relapse or reappearance. This particularly occurs with chemical peels because they work by temporarily removing cutaneous melanin, without having any effect on the melanogenesis process or melanocytes. So it requires the rational approach to treatment of using multiple chemical peel sessions (generally 5-6)at an interval of 2-4 weeks, combined with additional therapy for maintenance with chemical skin peel or by using a bleaching agent like hydroquinone, Kojic acid, topical vitamin C serum, tretinoin, which helps to further suppress melanin production.
Bottom line
Chemical skin peeling has evolved into an innovative and unique skin rejuvenation system. This evolution started with traditional peeling agents, such as AHAs, BHAs and TCA, and then progressed to the cocktail of skin peels like Jessner’s peel, which have remained popular for a long period of time. In their terms of effectiveness and safety, traditional GA peels have proved to be the best ones. Lactic acid peels, which are relatively less expensive, showed almost the same results as that of GA, but still need further research. Due to phytic acid peel’s unique properties, it may replace conventional AHAs, while the use of TCA peel in dark-skinned individuals still needs caution, as there are the risks of pigmentation dyschromias.
The trends of peeling are currently changing and the innovative cocktail peels which combine both skin brightening and rejuvenating ingredients are being effectively used for tackling pigmentation and signs of ageing, along with numerous other skin problems, such as acne, clogged pores, skin tone and texture, scarring, etc. They also help to stimulate new cell turnover.
The results of the skin peel depends on the type of peeling agent, including its concentration, frequency and how long it is applied. It is particularly important to provide advice to dark-skinned patientsabout photoprotection, priming agents and the importance of maintenance peels.
Lesley Fraser
Related Posts
We use cookies to give you the most relevant experience, Cookie Policy.

Botox & Dermal Filler Course
*excluding VAT

See What Our Fellows Have Been Up to Recently
Understanding depth, volume, and pressure can enhance a practitioner’s skill set, enabling them to provide more valuable services to their clients using their existing tools. #aestheticmedicine #dermalfillertraining #wrinklefree

Mastering hand stability isn’t magic, it’s a mix of experience & targeted learning 🎯 Our students get ahead with specialized techniques, paving the way for precise injections! 💉#SkillDevelopment #FutureHealthPros
.
.
.
.
.
#dermalfillertraining #aestheticmedicine #botoxtraining

Virtually any area can be reached using a cannula #fillertraining #aestheticmedicine #hsifellowprogram

“Unlock Your Aesthetic Potential with Harley Street Institute’s Fellowship! 🌟 Elevate your skills in aesthetic medicine through our intensive hands-on training in Botox and Dermal Fillers. Get ready to sculpt beauty, one injection at a time! 💉✨ Join us for a transformative learning journey that takes you beyond the classroom and into real-world expertise. Are you ready to master the art of enhancing natural beauty? 💫 #HarleyStreetFellowship #AestheticMedicineMastery #SculptingBeauty”

Link in bio
"Unlocking the Secrets of Masseter Botox: Empowering smiles, one injection at a time! 💉💪 Join me on an exciting journey as we delve into the world of Masseter Botox. Learn the art and science behind this transformative procedure, and discover how it can redefine facial aesthetics. Don`t miss out on this opportunity to enhance your skills and expand your practice. Let`s reshape faces and build confidence together!
Link in bio.
#MasseterBotoxCourse #FacialAesthetics #TransformativeProcedures #SmileEnhancement #ContinuingEducation
#aestheticmedicine

💭Have You Ever thought :
👉🏼What lies beneath the orbicularis oculi ?
👉🏼Why do I need to have the correct depth ?
👉🏼How to avoid an asymmetric smile, periorbital edema or a shelf like look at the lid/cheek junction ?
⚠️We all know that when treating crows feet, we are administering botox into the orbicularis oculi, and that there are complications but which and how?
‼️Too inferior or deep🟰 an asymmetric smile
(you’ve hit the zygomaticus minor muscle and major if you’re really too inferior!)
‼️Too medially 🟰 periorbital edema
(and you’re the periorbital region )
Located just underneath the skin, the orbicularis oculi has multiple origin and insertion points. A paired muscle, that overlies the periorbital region in a circular manner.
⚠️The wrong location, the wrong depth can result you injecting botox into a completely different muscle.

Welcome to the under eye region, an area of the face that can often show signs of aging such as wrinkles, hollows, and dark circles. Today, I want to share with you how fillers can be used to address these concerns by injecting them into different layers of the skin.
Using a needle, we can inject fillers into the dermis layer of the skin to improve the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. This can help to smooth out the texture of the skin and create a more youthful and refreshed look. However, it’s important to note that injecting fillers into this layer requires specialized training and experience to ensure safe and effective results.
In addition to the dermis layer, fillers can also be injected into the bone to help address deeper hollows and shadows under the eyes. This technique requires a higher level of expertise as it involves precise placement of the filler to achieve the desired outcome.
Lastly, fillers can be injected into the fat compartment of the under eye region using a cannula. This method can help to add volume and smooth out any irregularities in the fat pads under the eyes. Again, specialized training and experience are crucial for safe and effective results.
Overall, the use of fillers in the under eye region can provide a non-surgical solution to address signs of aging and enhance the appearance of the face. However, it’s important to seek out a qualified and experienced provider who has received proper training in the use of fillers in this delicate area.
If you’re interested in learning more about how fillers can benefit you, please don’t hesitate to reach out and schedule a consultation. Let’s work together to help you achieve your aesthetic goals!
#cosmedocs #harleystreetinstitute
.
.
.
.
#lifestyleblogger
#selfcarematters #aestheticmedicine
#beautytips
#skincarecommunity
#antiagingtips
#makeuptutorials
#selfcarelove
#aestheticbeauty
#lifestyleinspo #lifestyleblogger
#selfcarematters #dermalfillertraining
#beautytips
#skincarecommunity
#antiagingtips
#makeuptutorials
#selfcarelove #dermalfillers
#aestheticbeauty
#lifestyleinspo
#antiagingsecrets
#harleystreet #drahmedhaq #oxforduniversity
#harleystreetinstitute

The mentalis muscle is a facial muscle located in the chin area. It originates from the mandible and extends downward to the skin of the chin. The primary function of the mentalis muscle is to control the movement and position of the lower lip and the skin of the chin. It plays an important role in activities such as speaking, smiling, and pouting.
In addition to its role in facial expression, the mentalis muscle also helps to maintain the position of the lower front teeth and the shape of the lower lip. Dysfunction or hyperactivity of the mentalis muscle can lead to the development of chin wrinkles, which are vertical lines that appear on the skin of the chin. Understanding the anatomy and function of the mentalis muscle is important for healthcare providers when performing aesthetic procedures in the chin area.
Online Course With Video Demo
www.harleystreetinstitute.com
#botoxtraining #mentalistreatment

#Repost @dranabilamzavala with many thanks 🙏 and best wishes for the future.
Esta semana tuve la oportunidad de estar en Londres en una de las mejores clínicas con los mejores equipos de Medicina Estética en el mundo, perfeccionado técnicas de Rinomodelación con el Dr.Ahmed Haq.
——
@drahmedhaq You are simply incredible, thanks for the hands on and all the new techniques you shared. @drahmedhaq @harleystreetinstitute @cosmedocs
.
.
.
#aestheticmedicine #dermalfillertraining #nosejob #medicaltraining #plab #harleystreet #10harleystreet #aesthetics

Huge Congratulations to Mariana, on completing her foundation course in Aesthetics Medicine with us here at Harley Street Institute. 🥇✨
This combined course covers the necessities required for daily clinic practise, whether starting out or refreshing skills. Our small group training (4:1) provide unparalleled mentorship at any of our training days.
#cosmetictraining #aesthetics #hsi #cosmetics #cosmedocs #harleystreetcourses #foundationcourse #london

Only courses with true mentorship. #botoxtraining #dermalfillertraining #aestheticmedicine #hsifellowprogram #harleystreetfellowship

Huge congratulations to @onemedicalclinic for completing her Fellowship in aesthetic Medicine with us at Harley Street Institute 💫💫✨ We are so proud of having you 🥰
#Repost
Dr Crystal:”When I completed medical school 13 years ago, one of my cherished mentors gave me advice that has stayed with me for life - “never stop learning; it makes the difference between being good and being great."
From my years of Ophthalmic-surgical training to becoming a student of Public Health to my experience as a legislator in Parliament to operating my own
Medical and Aesthetic Medical practice, the lessons learned have been varied and valuable. 🤓
On this occasion my commitment to lifelong learning led me to Harley Street, London. I didn’t just want to be a good injector, I needed to be a great one so I needed to go where the great injectors were. 💉
Every day for the last two months I was immersed in one-on-one intensive training with the aim of mastering my injectable skills and thanks to the incredible team of doctors and trainers at @cosmedocs
@harleystreetinstitute l am proud to say Mission Accomplished! “

Huge Congratulations to Dale Rae for completing the Certificate in Aesthetic Medicine training program. 💫💫
💉The 3-day Aesthetic Medicine Certificate is tailored towards new practitioners who are ready to kick-start their career in Aesthetic Medicine. It aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the Layers of the Skin and Biological Ageing Process. The package also includes our most popular Foundation Botulinum Toxin and Dermal Fillers course, including an introduction to using cannula.
💉It is an Intense 3-day course incorporating essentials basic and advanced botox and dermal filler procedures combined with popular skin treatments perfect for the beginner all-rounded aesthetic practitioner.
You will be provided direct mentorship by our various cosmetic practitioners who are experts in performing their respective aesthetic treatments.
💉Small group training under the direct supervision of our experienced aesthetic trainers. Master procedures to an advanced level. Learn theory, consultation methods and manage client expectations as well as complications.
🙌 DM for more details. #aesthetic #dermalfillers #detmalfillertraining

Aesthetic medicine is an art. It`s not enough to know facial anatomy or to be a good injector. The best aesthetic doctor has an artistic eye. Sometimes this is a skill that can be developed over years. Being able to assess a fa ce within seconds of walking into a room. Knowing exactly how injectables can be used for subtle and natural results.
The end result should not be obvious to an untrained eye.
It`s such a shame to see overfilled faces exaggerating proportions. When really, the main aims are to restore volume lost or correct natural imbalances.
#aestheticmedicine #dermalfillers #beauty
Repost @cosmedocs

Huge Congratulations to @erikatydermatology for completing her Fellowship in Aesthetic Medicine with us at the Harley Street Institute 💫💫💫
Our Aesthetic Fellowship is the pinnacle of training for those seriously interested in escalating their careers.
.
Our fellows are taken on board within clinic over 3 months with weekend workshops, 1-1 mentoring, treatment log book and clinical assistance.
.
Following on from this they have the opportunity to have Independent Fellow Clinics to improve their confidence with patient consultation and individual treatment planning.
.
We believe that this is the future of aesthetic traning to ensure that practitioners have captured all the essential skills for successful careers.
.
We have been extremely proud of our old fellows, many who have moved on to now work with some of the most prestigious clinics in London.
.
Next enrolment periods: TBC
.
To find out more information or to apply, please email your CV to [email protected]
.
#thefellowship #harleystreetinstitute #doctorsanddentists

KISS
As the years some procedures get unnecessarily more complicated without much added benefits. Risks / complications have increased: more inexperienced practitioners , inadequate techniques, increasing consumer demand for bolder augmentation.
#keepitsimplestupid








Note: if you did not get the email, please check spam/junk folder